Install Kubernetes
Add sources(both cloud/edge)
curl -s https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
cat > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list <<EOF
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/apt/ kubernetes-xenial main
EOF
sudo apt-get update
Install Kubernetes components (cloud)
Install the following software packages on the cloud:
kubeadm:used to initialize the cluster.kubelet:used to launch pods on each node in the cluster.kubectl:command-line tool used to communicate with the cluster.
See the corresponding Kubernetes and KubeEdge versions at kubeedge/kubeedge.
# Check software version
apt-cache madison kubeadm
# Install the corresponding version of k8s components: kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet=1.22.2-00 kubeadm=1.22.2-00 kubectl=1.22.2-00
# Lock version
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Start Kubernetes cluster (cloud)
This step may occur Question 1: kube-proxy report iptables problems, Question 2: calico and coredns are always in initializing state and Question 3:metrics-server keeps unsuccessful state.
Reset environment (Skip on first installation)
swapoff -a
kubeadm reset
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker kubelet
rm -rf $HOME/.kube/config
rm -f /etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf # Delete k8s configuration file
rm -f /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt # Delete k8s certificate
rm -rf /etc/cni/net.d/ # Delete network configuration
iptables -F && iptables -t nat -F && iptables -t mangle -F && iptables -X
Initialize Kubernetes cluster
kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16 \
--image-repository registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
# If there is only one node, it needs to accommodate the stain.
kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/master node-role.kubernetes.io/master-
Download and configure calico (cloud)
In the Kubernetes cluster, pods are distributed across different hosts. To enable inter-host communication for these pods, it is necessary to install the CNI network plugin, and here, Calico network is chosen.
(After the k8s cluster is initialized, if you do not configure calico and other related network plugins,
you will find that coredns is always in a pending or containerCreating state.
Through kubectl describe, you will find that there is a lack of network components.)
Step 1: Download YAML for configuring calico network on master.
# pay attention to the corresponding version, v1.22 and v3.20
wget https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.20/manifests/calico.yaml --no-check-certificate
Step 2: Modify the pod network in calico.yaml.
# Change the pod network in 'calico.yaml' to the segment specified by the option '--pod-network-cidr' during kubeadm init.
# Use vim to open 'calico.yaml' and find '192'. Modify as following:
# no effect. This should fall within `--cluster-cidr`.
# - name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR
# value: "192.168.0.0/16"
# Disable file logging so `kubectl logs` works.
- name: CALICO_DISABLE_FILE_LOGGING
value: "true"
# Remove the two '#' symbols and the spaces following them, and change 192.168.0.0/16 to 10.244.0.0/16, as follows:
# no effect. This should fall within `--cluster-cidr`.
- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR
value: "10.244.0.0/16"
# Disable file logging so `kubectl logs` works.
- name: CALICO_DISABLE_FILE_LOGGING
value: "true"
Step 3: Pre-download the required images.
Check images used in 'calico.yaml':
grep image calico.yaml
# image: calico/cni:v3.20.6
# image: calico/cni:v3.20.6
# image: calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.20.6
# image: calico/node:v3.20.6
# image: calico/kube-controllers:v3.20.6
In the master node, download the aforementioned image.
# Pull image (change the version if needed)
for i in calico/cni:v3.20.6 calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.20.6 calico/node:v3.20.6 calico/kube-controllers:v3.20.6 ; do docker pull $i ; done
Calico only needs to exist on the master node.
Step 4: Start calico.
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml
# Check pod state (should in running)
kubectl get pods -A
Step 5: Configure calico and kube-proxy.
When an Edge node joins, calico-node and kube-proxy may be automatically deployed. Kube-proxy will deploy successfully (but the edgecore log will prompt that kube-proxy should not be deployed), and Calico will fail to initialize.
To avoid the above situation, perform the following operations:
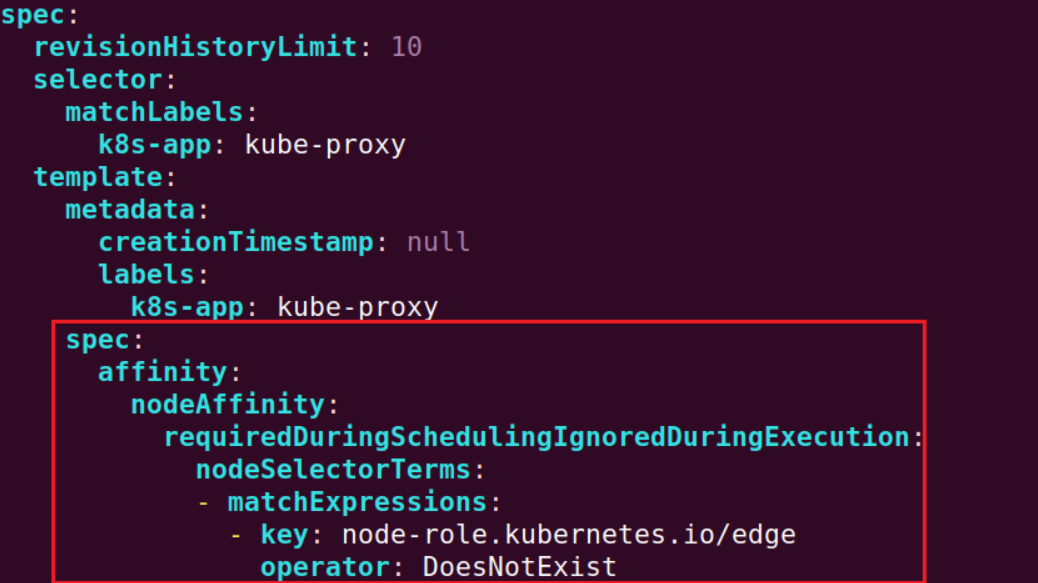
kubectl get daemonset -n kube-system | grep -v NAME | awk '{print $1}' |xargs -n 1 kubectl patch daemonset -n kube-system --type='json' -p='[{"op":"replace","path":"/spec/template/spec/affinity","value":{"nodeAffinity":{"requireDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution":{"nodeSelectorTerms":[{"matchExpressions":[{"key":"node-role.kubernetes.io/edge","operator":"DoesNotExist"}]}]}}}}]'
kubectl edit daemonset -n kube-system kube-proxy
# add the following content:
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/edge
operator: DoesNotExist
# add the same content in calico-node
kubectl edit daemonset -n kube-system calico-node
Use kubectl get pods -A to check if all calico related pods are running, and use kubectl logs [pod_name] -n [namespace] to check if there are any errors within the calico component.
Download and configure metrics-service (cloud)
Download metrics-service
metrics-service is used to track edge node logs, and installing metrics-service can help monitor cloud-edge distributed clusters.
There are official installation and local installation. If the official installation fails, you can try local installation.
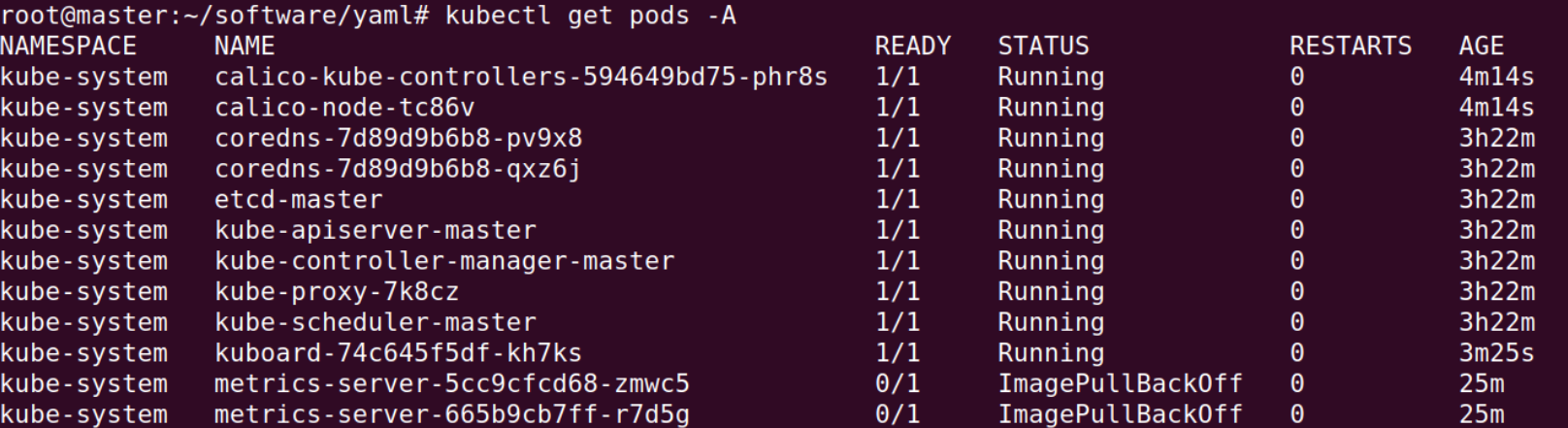
Official installation. (There may be errors for pulling images timeout.)
# Install metrics-service
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml
# Check pod state
kubectl get pods -A
Local installation.
First download the official YAML file.
wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml
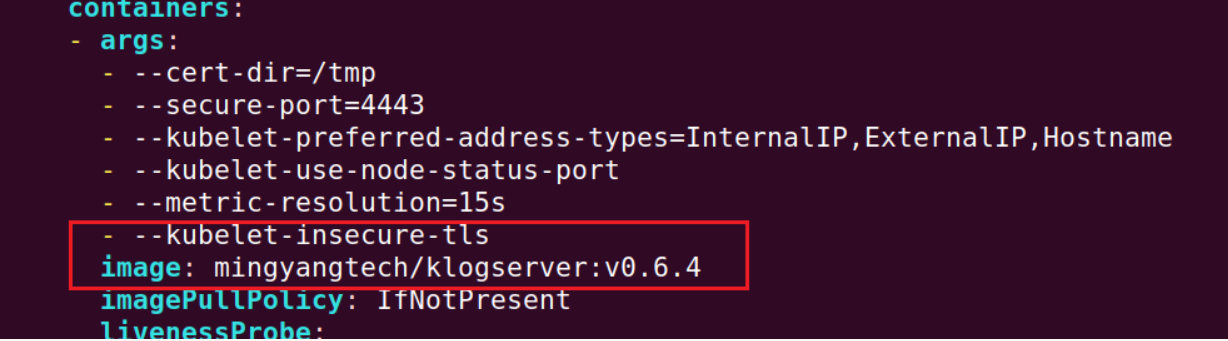
Check the official image version in components.yaml and search for the corresponding version of the unofficial image in dockerhub. Add - --kubelet-insecure-tls in the YAML file and modify the image name as follows:
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --metric-resolution=15s
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
image: mingyangtech/klogserver:v0.6.4
Install from the customized YAML file.
# Manually pull image
docker pull mingyangtech/klogserver:v0.6.4
# Install
kubectl apply -f components.yaml
Verify metrics-service
Verify the deployment of metrics-service.
kubectl top nodes